Sud medical abbreviation icd 10 plays a crucial role in diagnosing and managing Substance Use Disorder (SUD). This comprehensive guide delves into the definition, ICD-10 codes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of SUD, providing valuable insights for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking to understand this complex condition.
SUD encompasses a range of substance-related disorders, from alcohol and drug abuse to misuse of prescription medications. Understanding the specific ICD-10 codes used to diagnose SUD is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning.
SUD Definition and Description
Substance use disorder (SUD) is a chronic, relapsing brain disease that is characterized by compulsive drug-seeking and use, despite negative consequences. It is a complex condition that involves multiple factors, including genetics, environment, and social influences.
The key characteristics of SUD include:
- Inability to control drug use
- Preoccupation with drug use
- Continued use despite negative consequences
- Tolerance
- Withdrawal symptoms
SUD can be caused by a variety of substances, including alcohol, opioids, cocaine, and marijuana. However, any substance that can be abused has the potential to lead to SUD.
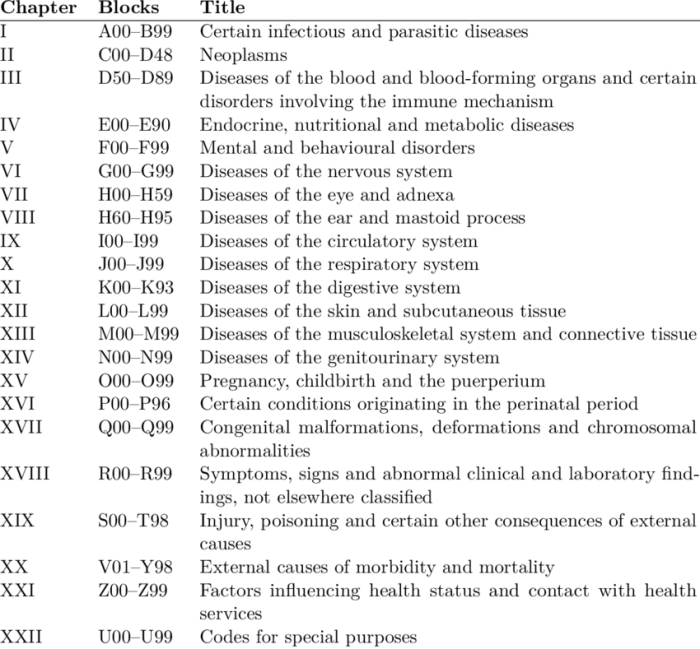
ICD-10 Codes for SUD
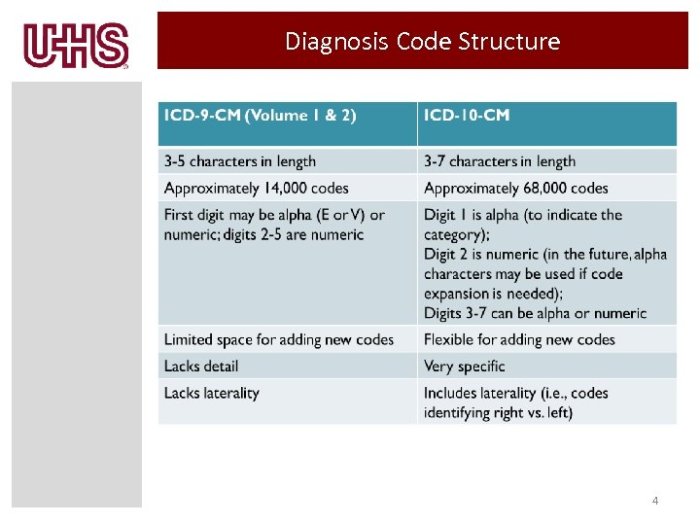
The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10) is a system of codes used to classify diseases and health conditions. There are several ICD-10 codes that can be used to diagnose SUD, depending on the specific substance involved and the severity of the disorder.
The most common ICD-10 codes for SUD are:
- F10.2: Alcohol dependence syndrome
- F11.2: Opioid dependence syndrome
- F12.2: Cocaine dependence syndrome
- F13.2: Cannabis dependence syndrome
The criteria for assigning each code are based on the following factors:
- The type of substance used
- The frequency and duration of use
- The severity of the symptoms
ICD-10 codes are used in clinical practice to diagnose SUD and to track the progress of treatment.
SUD Diagnosis and Assessment, Sud medical abbreviation icd 10
The diagnosis of SUD is based on a clinical evaluation that includes a physical exam, laboratory tests, and a psychological evaluation. The physical exam can help to identify any physical signs of drug use, such as needle marks or liver damage.
Laboratory tests can be used to detect the presence of drugs in the body.
The psychological evaluation is used to assess the patient’s mental health and to determine the severity of the SUD. The evaluation may include a review of the patient’s drug use history, a mental status exam, and a substance use disorder screening tool.
There are a number of different screening tools that can be used to identify SUD. Some of the most common tools include:
- The CAGE questionnaire
- The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT)
- The Drug Abuse Screening Test (DAST)
These tools can help to identify patients who may be at risk for SUD and who need further evaluation.
SUD Treatment and Management
The treatment of SUD is a complex process that requires a multidisciplinary approach. There is no one-size-fits-all treatment plan, and the best approach will vary depending on the individual patient’s needs.
The main goals of SUD treatment are to:
- Help the patient to achieve abstinence from drugs
- Reduce the risk of relapse
- Improve the patient’s quality of life
There are a number of different treatment options available for SUD, including:
- Medication
- Therapy
- Support groups
Medication can be used to help manage withdrawal symptoms, reduce cravings, and prevent relapse. Therapy can help the patient to learn about SUD, develop coping mechanisms, and change their behavior. Support groups can provide the patient with a safe and supportive environment where they can share their experiences and learn from others.
SUD Prevention and Education
SUD is a preventable condition. There are a number of risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing SUD, including:
- Early exposure to drugs
- Family history of SUD
- Mental health disorders
- Trauma
There are also a number of protective factors that can help to reduce the risk of developing SUD, including:
- Strong family relationships
- Positive peer relationships
- Good mental health
- Education about the risks of drug use
SUD prevention programs and education campaigns can help to reduce the risk of developing SUD by increasing awareness of the risks of drug use and by providing information about how to get help.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, Sud medical abbreviation icd 10 serves as a standardized language for healthcare professionals to diagnose and classify SUD. By understanding the definition, ICD-10 codes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of SUD, we can work towards reducing the burden of this prevalent condition and improving the lives of those affected.
Questions and Answers: Sud Medical Abbreviation Icd 10
What is the definition of SUD?
SUD refers to a pattern of problematic substance use that leads to significant impairment or distress in an individual’s life.
What are the different types of substances that can lead to SUD?
SUD can be caused by a wide range of substances, including alcohol, illicit drugs, prescription medications, and inhalants.
How are SUD diagnoses made?
SUD diagnoses are made based on specific criteria Artikeld in the ICD-10, which includes assessing substance use patterns, physical symptoms, and psychological factors.