How many neurons are in the brain? It’s a question that has fascinated scientists and philosophers for centuries. The human brain is an incredibly complex organ, and the number of neurons it contains is staggering. In this article, we’ll explore the average number of neurons in the human brain, the variation in neuron count among individuals, and the factors that influence neuron count.
The average adult human brain contains about 86 billion neurons. However, this number can vary significantly from person to person. Some people may have as few as 60 billion neurons, while others may have as many as 100 billion. The number of neurons in the brain is thought to be influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle.
Number of Neurons in the Brain
The human brain, the control center of our nervous system, is an intricate organ composed of billions of neurons. These neurons, the fundamental units of the brain, are responsible for transmitting information, processing thoughts, and regulating bodily functions.
On average, the adult human brain is estimated to contain approximately 86 billion neurons. However, this number can vary significantly among individuals, ranging from around 80 billion to over 100 billion neurons. Factors such as genetics, environmental influences, and individual experiences can contribute to these variations.
Factors Influencing Neuron Count
- Genetics:Genetic factors play a role in determining the number of neurons an individual is born with. Specific genes have been linked to variations in neuron count, influencing brain development and function.
- Environmental Influences:The environment can impact neuron count, particularly during early development. Exposure to certain toxins, nutritional deficiencies, or traumatic experiences can affect neuron growth and survival.
- Individual Experiences:Learning, cognitive activities, and social interactions can influence neuron count. Engaging in mentally stimulating activities, such as reading, problem-solving, and socializing, has been associated with increased neuron growth and preservation.
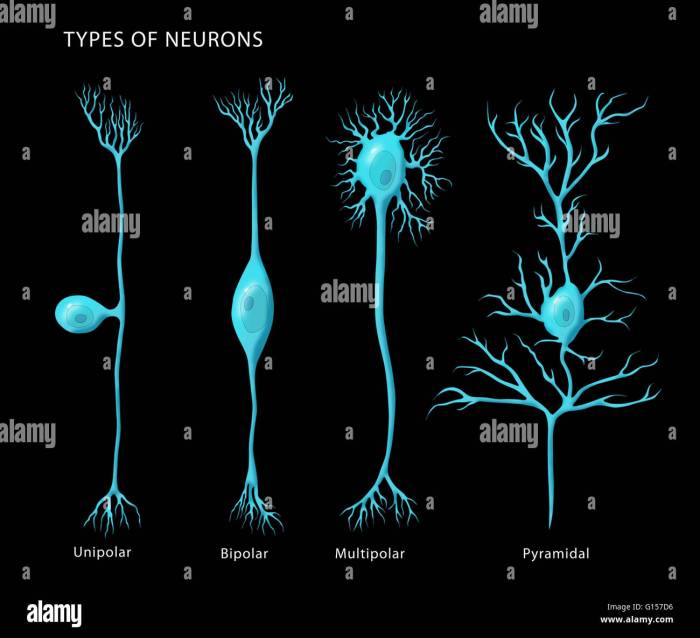
Types of Neurons
Neurons are the fundamental units of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting information throughout the brain and body. There are billions of neurons in the human brain, each with a unique structure and function. Neurons can be classified into several types based on their morphology, function, and location.
Morphological Classification
- Unipolar neurons:Have a single process that extends from the cell body, which then branches into two or more axons.
- Bipolar neurons:Have two processes that extend from the cell body, one axon and one dendrite.
- Multipolar neurons:Have multiple processes that extend from the cell body, including one axon and several dendrites.
Functional Classification
- Sensory neurons:Receive stimuli from the environment and transmit them to the central nervous system.
- Motor neurons:Transmit signals from the central nervous system to muscles and glands, causing them to contract or secrete substances.
- Interneurons:Connect neurons within the central nervous system, processing and relaying information.
Location-Based Classification, How many neurons are in the brain
- Central neurons:Located within the brain and spinal cord.
- Peripheral neurons:Located outside the brain and spinal cord, in the nerves and ganglia.
The following table summarizes the different types of neurons, their characteristics, and their roles:
| Type | Morphology | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unipolar | Single process | Sensory | Peripheral |
| Bipolar | Two processes | Sensory | Retina |
| Multipolar | Multiple processes | Motor, interneuron | Central and peripheral |
| Sensory | – | Receive stimuli | Peripheral |
| Motor | – | Transmit signals to muscles and glands | Central |
| Interneuron | – | Process and relay information | Central |
| Central | – | – | Brain and spinal cord |
| Peripheral | – | – | Nerves and ganglia |
Neuron Structure
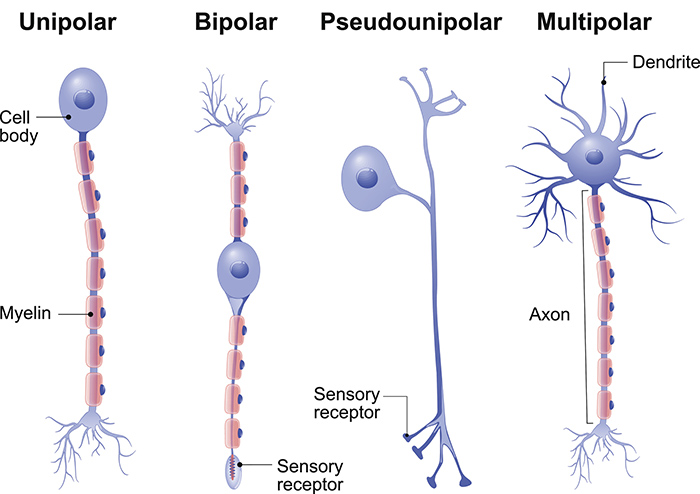
Neurons, the fundamental units of the nervous system, exhibit a complex and specialized structure that enables them to transmit and process information efficiently. The basic structure of a neuron consists of three main components: the cell body, dendrites, and axon.
Cell Body
The cell body, also known as the soma, is the central part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus, which houses the genetic material (DNA), and various organelles responsible for cellular functions such as protein synthesis and energy production.
Dendrites
Dendrites are short, branched extensions that extend from the cell body. They receive signals from other neurons and transmit them towards the cell body. Dendrites increase the surface area of the neuron, allowing it to receive input from multiple sources simultaneously.
Axon
The axon is a long, slender projection that extends from the cell body. It transmits signals away from the cell body to other neurons or target cells. The axon is covered by a myelin sheath, which acts as an insulating layer to speed up signal transmission.

Neuron Communication: How Many Neurons Are In The Brain
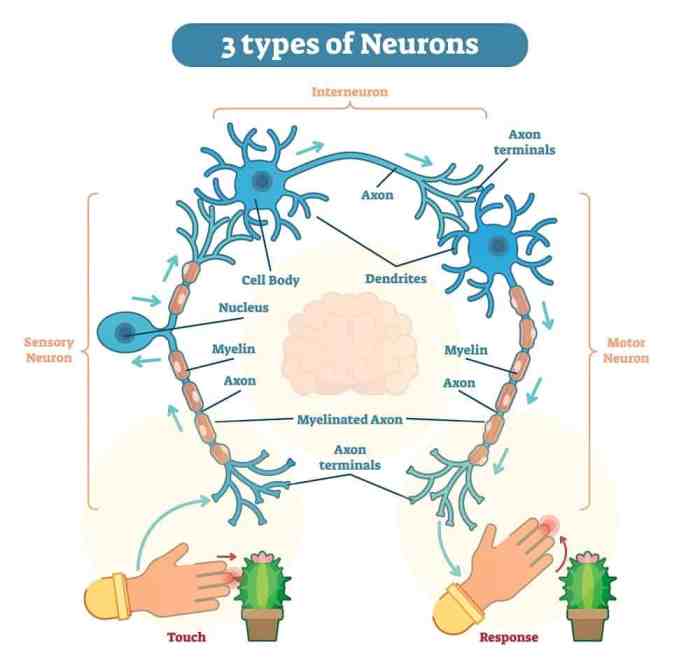
Neurons communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals. Electrical signals are generated by the movement of ions across the neuron’s membrane, while chemical signals are transmitted through neurotransmitters.
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that are released from the presynaptic neuron and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. This binding triggers a change in the electrical potential of the postsynaptic neuron, which can either excite or inhibit it.
Types of Neurotransmitters
- Glutamateis the most common excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. It is involved in learning and memory.
- GABAis the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. It is involved in reducing anxiety and promoting sleep.
- Dopamineis involved in reward and motivation.
- Serotoninis involved in mood and appetite.
- Norepinephrineis involved in attention and arousal.
Brain Regions and Neuron Density
The human brain is a complex organ composed of various regions, each with a distinct function. These regions exhibit variations in neuron density, which is the number of neurons per unit volume. Understanding these variations is crucial for comprehending the functional significance of different brain areas.
Cortical and Subcortical Regions
The cerebral cortex, the outermost layer of the brain, has the highest neuron density among all brain regions. It is responsible for higher-order cognitive functions such as perception, thinking, and language. In contrast, subcortical regions, such as the brainstem and cerebellum, have lower neuron densities but play essential roles in basic functions like motor control and balance.
Variation in Neuron Density
Neuron density varies significantly across different cortical areas. Primary sensory and motor areas, which process specific sensory or motor information, have higher neuron densities compared to association areas, which integrate and process information from multiple sensory modalities.
Functional Significance
Variations in neuron density reflect the functional specialization of different brain regions. Areas with high neuron density are capable of processing a large volume of information, enabling complex cognitive functions. Conversely, regions with lower neuron density are optimized for more specialized tasks.
Table: Neuron Density in Different Brain Regions
| Brain Region | Neuron Density (neurons/mm³) |
|---|---|
| Cerebral Cortex (Primary Sensory and Motor Areas) | 100,000-200,000 |
| Cerebral Cortex (Association Areas) | 50,000-100,000 |
| Hippocampus | 70,000-100,000 |
| Brainstem | 10,000-20,000 |
| Cerebellum | 20,000-50,000 |
Final Review
The number of neurons in the brain is a fascinating topic that has been studied by scientists for centuries. As we continue to learn more about the brain, we will gain a better understanding of how it works and how to keep it healthy.
Query Resolution
How many neurons are in the human brain?
The average adult human brain contains about 86 billion neurons.
What are the different types of neurons?
There are many different types of neurons, each with its own unique function. Some of the most common types of neurons include pyramidal neurons, stellate neurons, and interneurons.
What is the function of neurons?
Neurons are responsible for transmitting information throughout the brain. They do this by sending electrical signals to each other.
What are the factors that influence neuron count?
The number of neurons in the brain is thought to be influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle.