Emergency medical services (EMS) are the backbone of healthcare systems, providing life-saving care in critical situations. From ambulance services to trauma centers, EMS encompasses a comprehensive network of components that work together seamlessly to save lives and improve outcomes.
The diverse range of EMS personnel, including paramedics, emergency medical technicians (EMTs), and dispatchers, play crucial roles in delivering timely and effective care. Advanced medical devices, communication systems, and specialized vehicles ensure that patients receive the highest level of treatment at the scene of an emergency and during transportation to medical facilities.
Definition and Scope of Emergency Medical Services

Emergency medical services (EMS) are a critical component of the healthcare system, providing immediate and specialized care to individuals experiencing medical emergencies.
EMS encompasses a wide range of services, including:
- Responding to 911 calls and providing emergency care at the scene
- Transporting patients to hospitals or other medical facilities
- Providing ongoing medical care during transport
EMS is typically divided into three levels of care:
- Basic Life Support (BLS):Provides basic first aid and CPR
- Advanced Life Support (ALS):Provides more advanced medical care, including intubation and medication administration
- Critical Care Transport (CCT):Provides specialized care for critically ill or injured patients during transport
EMS plays a vital role in the healthcare system by providing immediate and potentially life-saving care to patients in emergency situations.
Components of Emergency Medical Services

Emergency Medical Services (EMS) encompass a comprehensive system designed to provide prompt and efficient medical care during emergencies. The system comprises several interconnected components, each playing a crucial role in delivering timely and effective medical interventions.
Ambulance Services
Ambulance services are the primary means of transporting patients to and from emergency departments. These services are equipped with trained paramedics and emergency medical technicians (EMTs) who provide immediate medical care during transport. Ambulance services operate 24/7, ensuring rapid response to medical emergencies.
Emergency Departments
Emergency departments (EDs) are hospital units dedicated to providing immediate medical attention to patients with acute illnesses or injuries. EDs are staffed by emergency physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals who assess, stabilize, and treat patients. EDs play a critical role in the initial management of medical emergencies and often determine the course of further treatment.
Trauma Centers
Trauma centers are specialized medical facilities designed to provide comprehensive care for patients with severe injuries. These centers are equipped with advanced medical equipment and highly trained trauma surgeons, nurses, and other healthcare professionals. Trauma centers provide specialized care for injuries such as head trauma, spinal cord injuries, and severe burns.
Communication Systems
Communication systems are essential for coordinating the various components of EMS. These systems allow dispatchers to receive and prioritize emergency calls, communicate with ambulance crews, and facilitate communication between healthcare providers at different locations. Effective communication systems ensure that patients receive timely and appropriate medical care.
Operations and Procedures
Emergency medical services (EMS) operations and procedures encompass a range of activities designed to provide timely and efficient medical care to individuals in need. These procedures are crucial for ensuring the safety and well-being of patients during medical emergencies.
The typical operations and procedures of EMS include:
Dispatch and Triage, Emergency medical services
When an emergency call is received, a dispatcher gathers information about the incident and the patient’s condition. Based on this information, the dispatcher determines the appropriate level of response and dispatches the nearest EMS unit to the scene.
Patient Assessment and Treatment
Once the EMS unit arrives at the scene, paramedics or emergency medical technicians (EMTs) conduct a thorough assessment of the patient’s condition. This assessment includes taking vital signs, examining the patient for injuries or medical conditions, and obtaining a medical history.
Based on the assessment, the EMS team provides appropriate medical treatment, which may include administering medications, splinting fractures, or providing oxygen.
Transportation and Handover
If the patient requires further medical care, the EMS team will transport the patient to the nearest appropriate hospital. During transport, the EMS team continues to monitor the patient’s condition and provides any necessary medical interventions. Upon arrival at the hospital, the EMS team will handover the patient to the hospital staff, providing a detailed report of the patient’s condition and any treatment provided.
Technology and Equipment
In emergency medical services (EMS), advanced technology and equipment play a pivotal role in enhancing patient care and improving the efficiency of emergency response.
These technologies and equipment range from sophisticated medical devices to cutting-edge communication systems and specialized vehicles.
Medical Devices
EMS professionals utilize various medical devices to assess, monitor, and treat patients during emergencies. These devices include:
- Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs):Portable devices that deliver electrical shocks to restore normal heart rhythm in cardiac arrest patients.
- Patient Monitors:Devices that track vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels.
- Portable Ventilators:Mechanical devices that assist breathing in patients with respiratory distress.
- Medication Dispensing Systems:Devices that accurately and safely administer medications.
Communication Systems
Effective communication is crucial in EMS. Advanced communication systems facilitate seamless coordination between emergency responders and medical facilities:
- Two-Way Radios:Portable devices that allow EMS personnel to communicate with each other and with dispatchers.
- Mobile Data Terminals (MDTs):Computerized systems that provide access to patient information, maps, and navigation tools.
- Satellite Communication:Enables communication in remote areas or during disasters.
Vehicles and Equipment
EMS vehicles are equipped with specialized equipment and supplies to provide immediate medical care at the scene of an emergency:
- Ambulances:Equipped with life-saving equipment and transport capabilities for patients.
- First Response Vehicles:Smaller vehicles used for rapid response and initial assessment.
- Medical Equipment:Includes stretchers, oxygen tanks, bandages, and other essential supplies.
Personnel and Training
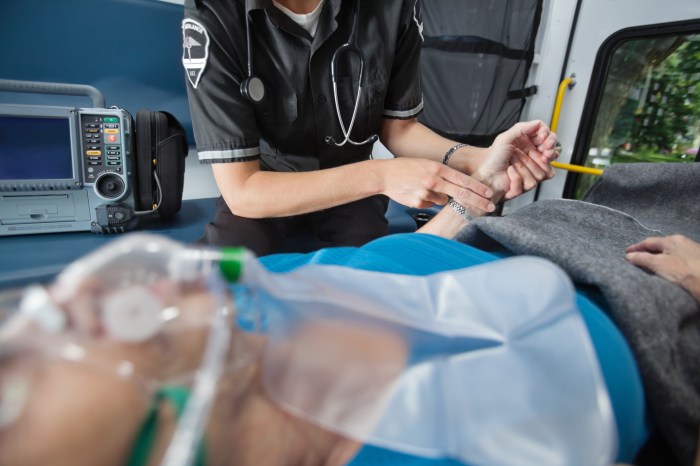
Emergency Medical Services (EMS) personnel play a critical role in providing prompt and effective medical care to patients in emergency situations. They are trained to assess, stabilize, and transport patients to appropriate medical facilities. There are various types of EMS personnel, each with specific roles and responsibilities.
Types of EMS Personnel
- Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs):EMTs provide basic life support (BLS), which includes CPR, first aid, and oxygen administration. They are typically the first responders to medical emergencies and work under the supervision of paramedics or physicians.
- Paramedics:Paramedics are advanced life support (ALS) providers who can administer medications, perform advanced medical procedures, and use specialized equipment. They work in close collaboration with physicians and other healthcare professionals.
- Emergency Physicians:Emergency physicians are medical doctors who specialize in emergency medicine. They provide medical direction to EMS personnel and oversee the care of patients in emergency departments.
- Nurses:Nurses play a vital role in EMS, providing nursing care to patients in emergency settings. They assist with patient assessment, treatment, and transportation.
Training and Certification
EMS providers must undergo rigorous training and certification programs to ensure they possess the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their duties effectively. The specific training requirements vary depending on the level of certification.
- EMTs:EMT training programs typically include coursework in anatomy, physiology, first aid, CPR, and patient assessment. Upon completion of the program, EMTs must pass a national certification exam.
- Paramedics:Paramedic training programs are more advanced and include additional coursework in pharmacology, advanced medical procedures, and patient management. Paramedics must also pass a national certification exam.
- Emergency Physicians:Emergency physicians complete medical school and residency training in emergency medicine. They must also pass a board certification exam to practice emergency medicine.
- Nurses:Nurses who work in EMS typically have a nursing degree and additional training in emergency nursing. They may also obtain certification in emergency nursing.
Continuing Education and Professional Development
Continuing education and professional development are essential for EMS providers to stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in emergency medicine. They can attend conferences, workshops, and online courses to enhance their skills and knowledge. Many EMS agencies also provide in-house training programs to ensure their personnel are well-trained and proficient.
Quality and Performance Improvement
Quality and performance improvement are crucial in Emergency Medical Services (EMS) as they directly impact patient outcomes, resource utilization, and overall system effectiveness.
EMS providers continuously strive to enhance the quality of care they provide. This involves measuring and analyzing performance indicators, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing strategies to enhance patient outcomes.
Methods to Measure and Improve EMS Outcomes
- Clinical outcome measures:These assess patient health status and well-being, such as survival rates, hospital admission rates, and functional status.
- Process measures:These evaluate the quality of care processes, such as response times, treatment protocols, and patient satisfaction.
- System measures:These assess the overall effectiveness and efficiency of the EMS system, such as resource allocation, coordination with other healthcare providers, and community outreach.
EMS providers use various tools and techniques to measure and improve outcomes, including data collection, performance audits, and quality improvement initiatives.
Accreditation and Certification in EMS
Accreditation and certification play a vital role in EMS quality improvement. Accreditation bodies, such as the Commission on Accreditation of Ambulance Services (CAAS), set standards for EMS providers to ensure they meet specific quality benchmarks.
Certified EMS professionals demonstrate their knowledge and skills through rigorous training and testing. Certification programs help ensure that EMS providers are competent and up-to-date with the latest best practices.
Challenges and Future Directions
Emergency medical services (EMS) face numerous challenges that affect their ability to provide timely and effective care. These challenges include increasing demand for services, limited resources, and a changing healthcare landscape.
Increasing Demand for Services
The demand for EMS services is growing due to factors such as an aging population, increased chronic diseases, and the opioid epidemic. This increased demand is putting a strain on EMS resources and making it difficult to meet the needs of patients.
Limited Resources
EMS providers are often faced with limited resources, including funding, personnel, and equipment. This can make it difficult to provide the best possible care to patients. In some cases, EMS providers may have to make difficult decisions about who to treat and how to allocate resources.
Changing Healthcare Landscape
The healthcare landscape is constantly changing, and EMS providers must be able to adapt to these changes. These changes include the increasing use of telemedicine, the development of new technologies, and the changing role of EMS in the healthcare system.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions in EMS
Despite the challenges, there are also a number of emerging trends and future directions in EMS that are promising. These trends include the use of new technologies, the development of new care models, and the increasing focus on quality and performance improvement.
Final Wrap-Up
EMS continues to evolve, embracing technological advancements and innovative approaches to meet the ever-changing healthcare landscape. As demand for services grows, EMS providers are adapting to ensure that communities have access to the critical care they need. By investing in quality improvement initiatives and fostering collaboration among healthcare professionals, EMS is poised to continue delivering exceptional care and saving lives in the years to come.
Questions and Answers: Emergency Medical Services
What is the primary purpose of emergency medical services?
EMS provides immediate medical care and transportation to individuals experiencing medical emergencies or traumatic injuries.
What are the different levels of EMS care?
EMS care is typically divided into three levels: basic life support (BLS), advanced life support (ALS), and paramedic level care.
Who is responsible for dispatching emergency medical services?
Emergency medical dispatchers receive and triage emergency calls, determining the appropriate level of response and dispatching the nearest available EMS unit.